1 Vulnerability Required Manual Review and Could Not Be Updated
Table of contents
- Most security audits
- Running a security audit with npm audit
- Resolving EAUDITNOPJSON and EAUDITNOLOCK errors
- Reviewing and acting on the security audit written report
- Security vulnerabilities plant with suggested updates
- SEMVER warnings
- Security vulnerabilities found requiring manual review
- Check for mitigating factors
- Update dependent packages if a fix exists
- Fix the vulnerability
- Open an issue in the package or dependent package issue tracker
- No security vulnerabilities found
- Security vulnerabilities plant with suggested updates
- Turning off npm inspect on parcel installation
- Installing a unmarried parcel
- Installing all packages
About security audits
A security audit is an cess of package dependencies for security vulnerabilities. Security audits assist y'all protect your package's users by enabling yous to find and gear up known vulnerabilities in dependencies that could crusade information loss, service outages, unauthorized admission to sensitive information, or other issues.
Running a security audit with npm audit
Annotation: The npm audit command is bachelor in npm@6. To upgrade, run npm install npm@latest -g.
The npm inspect command submits a description of the dependencies configured in your packet to your default registry and asks for a report of known vulnerabilities. npm audit checks direct dependencies, devDependencies, bundledDependencies, and optionalDependencies, but does non check peerDependencies.
npm audit automatically runs when you install a package with npm install. You can also run npm audit manually on your locally installed packages to conduct a security audit of the package and produce a study of dependency vulnerabilities and, if available, suggested patches.
- On the control line, navigate to your package directory past typing
cd path/to/your-package-proper nameand pressing Enter. - Ensure your package contains
package.jsonandpackage-lock.jsonfiles. - Blazon
npm auditand press Enter. - Review the inspect report and run recommended commands or investigate further if needed.
Resolving EAUDITNOPJSON and EAUDITNOLOCK errors
npm audit requires packages to have package.json and package-lock.json files.
- If yous go an
EAUDITNOPJSONerror, create abundle.jsonfile past post-obit the steps in "Creating a bundle.json file". - If you go an
EAUDITNOLOCKerror, make sure your package has apacket.jsonfile, then create the bundle lock file by runningnpm i --package-lock-only.
Reviewing and acting on the security inspect written report
Running npm audit will produce a written report of security vulnerabilities with the affected packet name, vulnerability severity and description, path, and other information, and, if available, commands to use patches to resolve vulnerabilities. For more data on the fields in the inspect written report, see "About audit reports"
Security vulnerabilities found with suggested updates
If security vulnerabilities are found and updates are bachelor, you tin either:
- Run the
npm audit preparesubcommand to automatically install compatible updates to vulnerable dependencies. - Run the recommended commands individually to install updates to vulnerable dependencies. (Some updates may be semver-breaking changes; for more data, run across "SEMVER warnings".)
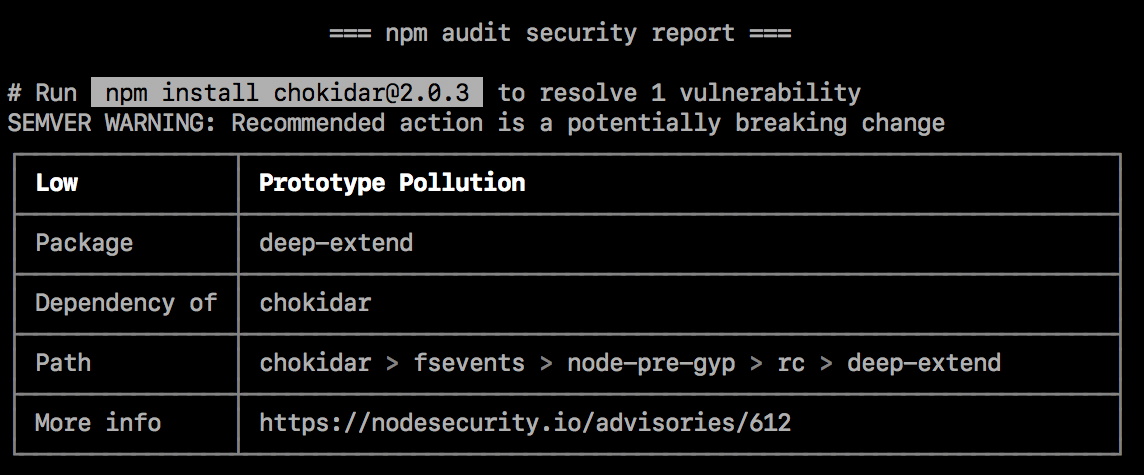
SEMVER warnings
If the recommended action is a potential breaking change (semantic version major change), it will be followed past a SEMVER WARNING that says "SEMVER WARNING: Recommended action is a potentially breaking alter". If the parcel with the vulnerability has changed its API, you may need to make additional changes to your package's code.
Security vulnerabilities constitute requiring transmission review
If security vulnerabilities are found, but no patches are available, the inspect written report will provide information about the vulnerability so yous can investigate further.
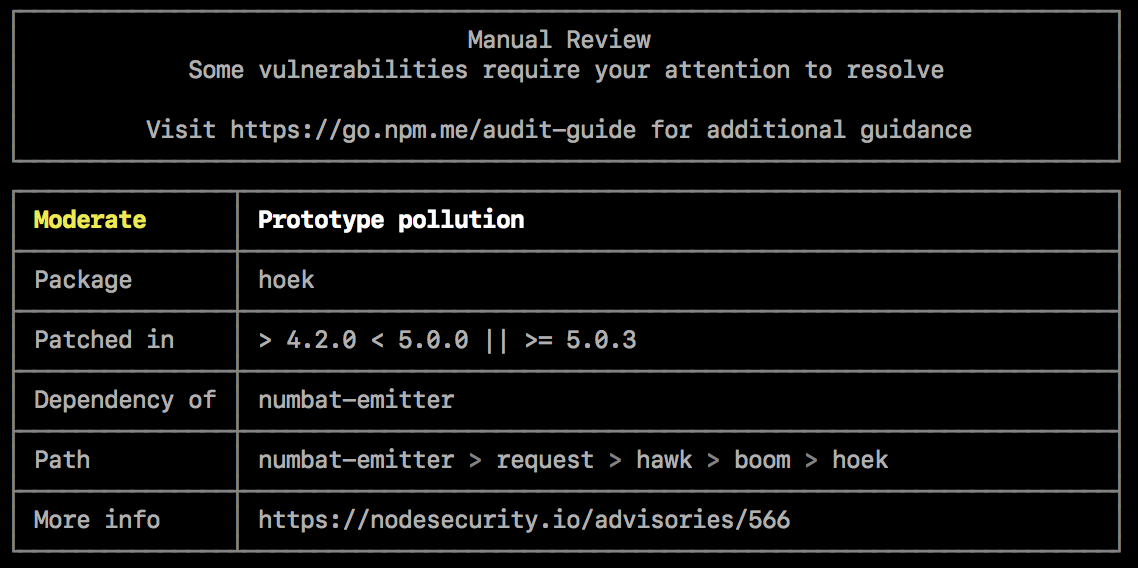
To address the vulnerability, you can
- Bank check for mitigating factors
- Update dependent packages if a gear up exists
- Prepare the vulnerability
- Open an effect in the package or dependent package issue tracker
Check for mitigating factors
Review the security advisory in the "More info" field for mitigating factors that may allow you lot to continue using the package with the vulnerability in limited cases. For example, the vulnerability may only exist when the code is used on specific operating systems, or when a specific function is chosen.
Update dependent packages if a gear up exists
If a fix exists but packages that depend on the packet with the vulnerability have non been updated to include the fixed version, yous may desire to open a pull or merge request on the dependent bundle repository to use the fixed version.
- To find the package that must exist updated, cheque the "Path" field for the location of the package with the vulnerability, then bank check for the parcel that depends on it. For example, if the path to the vulnerability is
@parcel-name > dependent-parcel > package-with-vulnerability, you will need to updatedependent-package. - On the npm public registry, find the dependent package and navigate to its repository. For more information on finding packages, run into "Searching for and choosing packages to download".
- In the dependent packet repository, open a pull or merge request to update the version of the vulnerable bundle to a version with a ready.
- Once the pull or merge asking is merged and the package has been updated in the npm public registry, update your re-create of the packet with
npm update.
Fix the vulnerability
If a set does not exist, y'all may want to suggest changes that address the vulnerability to the package maintainer in a pull or merge request on the parcel repository.
- Bank check the "Path" field for the location of the vulnerability.
- On the npm public registry, observe the package with the vulnerability. For more information on finding packages, see "Searching for and choosing packages to download".
- In the package repository, open a pull or merge asking to make the fix on the bundle repository.
- Once the fix is merged and the packet has been updated in the npm public registry, update your copy of the package that depends on the package with the fix.
Open an issue in the package or dependent package consequence tracker
If you lot do not want to fix the vulnerability or update the dependent package yourself, open an issue in the package or dependent packet outcome tracker.
- On the npm public registry, find the package with the vulnerability or the dependent bundle that needs an update. For more than information on finding packages, run into "Searching for and choosing packages to download".
- In the package or dependent package issue tracker, open an issue and include data from the audit written report, including the vulnerability report from the "More than info" field.
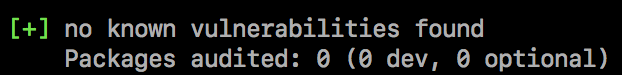
No security vulnerabilities found
If no security vulnerabilities are found, this means that packages with known vulnerabilities were not institute in your package dependency tree. Since the advisory database can be updated at any time, we recommend regularly running npm inspect manually, or calculation npm audit to your continuous integration procedure.
Turning off npm audit on parcel installation
Installing a unmarried package
To plow off npm inspect when installing a single package, apply the --no-audit flag:
npm install case-package-name --no-inspect
For more than information, see the npm-install command.
Installing all packages
To turn off npm audit when installing all packages, set the audit setting to false in your user and global npmrc config files:
For more than information, see the npm-config direction control and the npm-config audit setting.
Source: https://docs.npmjs.com/auditing-package-dependencies-for-security-vulnerabilities/
0 Response to "1 Vulnerability Required Manual Review and Could Not Be Updated"
ارسال یک نظر